Australia’s agricultural sector has always been a production powerhouse, producing billions of dollars’ worth of wheat, beef and veal, canola, cotton, and other agricultural products annually and staunchly contributing to Australia’s GDP.
The rise of digital industrial technologies has only strengthened the agriculture sector even further, allowing Aussie farmers to optimise their field operations and boost their yields year-on-year and with every additional investment in precision agricultural practices and equipment.
But what is precision agriculture exactly? And what digital transformation initiatives are poised to provide optimal investment returns for farmers? Our AgriTech specialists at Autonomous AG are here to answer just these questions today.
The History & Evolution of Precision Agriculture
In the beginning, precision agriculture was less about technology and more about methodology, with farmers developing ideal practices for maximising their output whilst minimising labour. This human ambition to make field work more manageable can be traced all the way back to 5500BC and the dawn of agriculture itself, with farmers inventing wooden ploughs designed to till soil faster and across larger harvest areas.
Thousands of years later during the Industrial Revolution, steam engine technology allowed for the invention of the world’s first tractor. The next 200 years from that day forth brought dizzyingly rapid developments.
Cut to today and the monumental innovations in digital technologies has changed our definition of precision agriculture to include the implementation of specialised industrial AgriTech – think autonomous tractors, smart irrigation systems, agricultural drones, AgBots and even technology we’ve been using for decades now, like electronic identification (EID) tagging for livestock.
Key Principles of Precision Agriculture
So what is precision agriculture? At its simplest definition, precision agriculture is a management strategy that revolves around utilising operational data to boost the volume, quality, efficiency, and overall sustainability of agricultural production processes. Precision agricultural practices are designed to gather, process, and analyse data across all processes of an agricultural production chain, from seed sowing to water management, harvesting, processing/packaging, and even transportation of goods.
By providing holistic insights, precision agricultural practices allow farmers to make highly focused decisions relating to the optimisation of their production processes, attaining desired results faster. Farmers can also verify those results and continue tracking process performance by using comprehensive data monitoring solutions that support precision agriculture technologies.
On top of utilising data monitoring processes, some of the other foundational principles of precision agriculture include geolocating, managing field variability, and implementing control strategies. All of these practices ensure optimal growing and facility conditions for farms, ensuring that farmers can establish and maintain production benchmarks that they can continue to hone with further performance monitoring.
The Precision Agriculture Cycle
Precision agricultural practices operate off of principles of continuous improvement. This means that the process of developing and maintaining precision agricultural practices follows a PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) model. Similarly, the precision agriculture is also a 4-step process:
-
- Data collection – at this stage, farmers must gather performance data through the use of precision agricultural technologies (i.e. IIoT devices, sensor technology, etc.)
- Data processing – this second stage includes the preprocessing, processing, and analysis of performance data.
- Data-driven decision-making – using the analysed data, farmers can now develop process optimisation strategies that further boost their precision agricultural practices.
- Process application – at the final stage, farmers can implement the new process components and continue measuring the performance of precision agricultural practices to monitor the impact of each incremental process improvement over time.
Emerging Precision Agriculture Technologies
As we’ve mentioned, there are some precision agriculture technologies we’ve already been using for years now, like EID tags for counting livestock heads. So the question as we enter the digital age is what precision agriculture technologies are poised to provide major gains for farmers over the next few decades?
Here are the emerging precision agriculture technologies that our AgriTech specialists agree should stay on everyone’s radar.
GPS & RTK Networks
By using GNSS satellite data, RTK (real-time kinetic positioning) GPS technology allows for improved accuracy when determining GPS positioning and GPS mapping. In agriculture industry use cases, RTK GPS mapping supports farmers in developing highly detailed field maps that take into account additional ground monitoring processes like landslide monitoring and detection.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Topography isn’t the only factor when determining the quality of a crop field. This is where GIS systems can support precision agricultural processes. By allowing farmers to accurately map and analyse holistic factors like soil composition, nutrient levels, water levels, and other soil characteristics, GIS systems help ensure fields provide the most optimal growing conditions prior to seed sowing, supporting higher yields and healthier crop outputs.
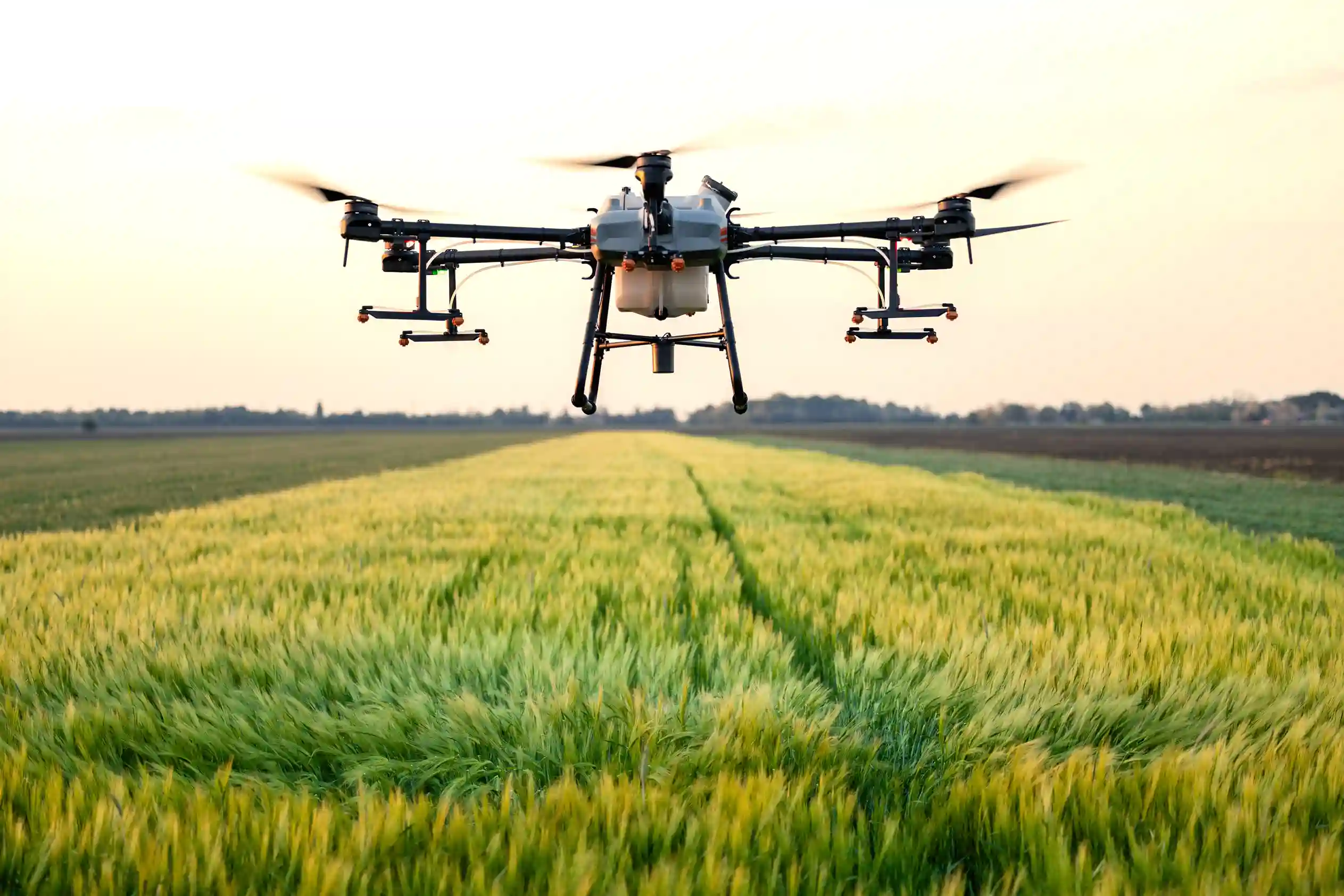
Remote Sensors & Aerial Technology
Agricultural drones are being used to monitor fields across all stages of the harvest cycle, from seed germination to crop harvesting. Similarly, remote sensors strategically installed across crop fields allow farmers to develop both satellite imagery via aerial drones, as well as detailed diagnostics mapping that can be used to monitor crop health and growth patterns in real-time and in comparison to historical data.
Variable Rate Technology (VRT) and Data Analytics
Farmers know all too well that even minute alterations to growing conditions (i.e. solar orientation, water levels, soil nutrients, etc.), can dramatically affect harvest output – especially in Australia, where farmers are already contending with volatile weather conditions. To support the macroscale monitoring efforts required for agricultural process optimisation, VRT technology supports farmers in running data simulations based on varying crop inputs.
Using this predictive analytical tech, farmers can determine within a margin of error what outcomes are likely to result from adding more fertiliser, changing irrigation patterns, varying the application of agricultural chemicals, or natural/seasonally occurring fluctuations in soil nutrient density.
Robotics & Machine Learning
IIoT technologies have been a staple of agricultural processes for most of the 21st century, but the development of machine learning and LLMs has allowed for even greater innovations in the realm of AgBots. Today, farmers across the globe are investing in industry robotics that use AI capabilities to maintain dynamic workflows and gather data across a range of data points. This operational data can then be interpreted autonomously by machine learning capabilities, providing farmers with tailored insights into all monitored aspects of their harvest operations.
Benefits of Precision Agriculture
At this point, the major benefits of precision agriculture technologies are already fairly easy to see. Some of these primary benefits include:
- Improved efficiency
- Enhanced crop yields
- Reduced labour
- Resource optimisation
- Improved plant sustainability
- Higher profit margins
All of these benefits help farmers conserve their operational costs and grow their profit margins, clearly demonstrating the return on investment available for farmers looking to invest in precision farming for their next digital transformation initiatives.
Harness the Power of Precision Agriculture for your Farms
At Autonomous AG, our vision is to support Aussie farmers in working smarter, not harder. That’s why we’ve developed our selection of precision agriculture products, all designed to streamline your farming operations and optimise your field gains.
From CHCNav’s autosteering tractor guidance systems to radio modems, GNSS base stations, iQuus autonomous tractor kits, and other AgriTech solutions, these precision agriculture investments will keep your farm not only digital-ready but continuously improving year-on-year – for decades to come.
Want to learn more about our precision agriculture solutions here at Autonomous AG? Get in touch with our AgriTech specialists to learn more about our product range, or find your nearest dealer to see our products in-store.